https://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=9&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwiN0fmo6-XSAhUEppQKHYODC5oQFghLMAg&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.elnusa.co.id%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2016%2F02%2FLaporan-Keuangan-Audit-per-31-Desember-2015.pdf&usg=AFQjCNHpJKxuiqxM28kUuhWLaE937tTdjg&sig2=OhzF1jYjQhWb7p7IKLwDKQ
Senin, 20 Maret 2017
Common size PT. Elnusa Tbk
https://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=9&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwiN0fmo6-XSAhUEppQKHYODC5oQFghLMAg&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.elnusa.co.id%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2016%2F02%2FLaporan-Keuangan-Audit-per-31-Desember-2015.pdf&usg=AFQjCNHpJKxuiqxM28kUuhWLaE937tTdjg&sig2=OhzF1jYjQhWb7p7IKLwDKQ
Senin, 13 Maret 2017
Independent Audit of Annual Report PT. INDOCEMENT TUNGGAL PRAKARSA Tbk.
Independent Auditor's Report
Report No. RPC-7004/PSS/2015
The Shareholders, the Boards of Commisioners and Directors
PT. Indocement Tunggal Prakarsa Tbk
We have audited the accompanying consolidated financial statements of PT indocement Tunggal Prakarsa Tbk ("the company") and its subsidiaries, which comprise the consolidated statement of financal position as of December 31, 2014, and the consolidated statements of comprehensive income, changes in equity, and cash flows for the year then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other expalanatory information.
Management's responsibility for the financial statement
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of such consolidated financial statement in accordance with indonesian Financial Accounting Standard, and for such internal control as management determines is necessary to enable the preparation of consolidated financial statements that are free from material misstatement, wheter due to fraud of error.
Auditor's responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on such consolidated financial statements based on our audit. we conducted our auditin accordance with standards on auditing established by the indonesian institute of certified public accountants. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether such consolidated financial statementsare free from material misstatement. an audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the Auditor's judgment, including the assesment of the risk of material misstatement of the financial statement, whether due to farud or error. in making those risk assesment, the auditor consider internal control relevant to the entity's preparation and fair presentation of the financial statementsin order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectuveness of the entity's internal control. an audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonablesness of accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements.
we believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our auidt opinion.
Opinion
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of PT Indocement Tunggal Prakarsa Tbk and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014, and their consolidated financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended, in accordance with Indonesian Financial Accounting Standards.
References :
https://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=6&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwia3e6NwtPSAhWHj5QKHTy_AqoQFgg0MAU&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.indocement.co.id%2Fv5%2FIndocementContent%2FAttachment%2FReport%2FFinancial%2520Report%2520and%2520Presentation%2FAudited%2520Report%2F12%2520Laporan%2520Keuangan%2520Konsolidasi%2520Tahun%2520Buku%25202014_INTP.pdf&usg=AFQjCNFWYnGELT03d5k0PazI6l6OCtVR9g&sig2=1OkgyurSqZEaF2sSAu6i4A
Member of group :
Wisnu Reno Wijaya/C1L014012
Erizal Wibisono S/C1L014026
Eko Fajar Sulaiman/C1L014032
Ilham A Pramuditya/C1L014033
Report No. RPC-7004/PSS/2015
The Shareholders, the Boards of Commisioners and Directors
PT. Indocement Tunggal Prakarsa Tbk
We have audited the accompanying consolidated financial statements of PT indocement Tunggal Prakarsa Tbk ("the company") and its subsidiaries, which comprise the consolidated statement of financal position as of December 31, 2014, and the consolidated statements of comprehensive income, changes in equity, and cash flows for the year then ended, and a summary of significant accounting policies and other expalanatory information.
Management's responsibility for the financial statement
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of such consolidated financial statement in accordance with indonesian Financial Accounting Standard, and for such internal control as management determines is necessary to enable the preparation of consolidated financial statements that are free from material misstatement, wheter due to fraud of error.
Auditor's responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on such consolidated financial statements based on our audit. we conducted our auditin accordance with standards on auditing established by the indonesian institute of certified public accountants. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether such consolidated financial statementsare free from material misstatement. an audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. The procedures selected depend on the Auditor's judgment, including the assesment of the risk of material misstatement of the financial statement, whether due to farud or error. in making those risk assesment, the auditor consider internal control relevant to the entity's preparation and fair presentation of the financial statementsin order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectuveness of the entity's internal control. an audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonablesness of accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements.
we believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our auidt opinion.
Opinion
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of PT Indocement Tunggal Prakarsa Tbk and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014, and their consolidated financial performance and cash flows for the year then ended, in accordance with Indonesian Financial Accounting Standards.
References :
https://www.google.co.id/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=6&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=0ahUKEwia3e6NwtPSAhWHj5QKHTy_AqoQFgg0MAU&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.indocement.co.id%2Fv5%2FIndocementContent%2FAttachment%2FReport%2FFinancial%2520Report%2520and%2520Presentation%2FAudited%2520Report%2F12%2520Laporan%2520Keuangan%2520Konsolidasi%2520Tahun%2520Buku%25202014_INTP.pdf&usg=AFQjCNFWYnGELT03d5k0PazI6l6OCtVR9g&sig2=1OkgyurSqZEaF2sSAu6i4A
Member of group :
Wisnu Reno Wijaya/C1L014012
Erizal Wibisono S/C1L014026
Eko Fajar Sulaiman/C1L014032
Ilham A Pramuditya/C1L014033
Minggu, 12 Maret 2017
Updated Internal Control Framework according to Coso
In 2013, the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) issued a comprehensive update to its original 1992 Internal Control - Integrated Framework. This COSO framework is the de facto framework used by more than 99 percent of the organizations required to comply with Section 404 - Internal Controls over Financial Reporting (ICFR) requirement of the Sarbanes-Oxley Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act (SOX).
COSO broadly defines enterprise risk management (ERM) as “The culture, capabilities and practices integrated with strategy-setting and its execution, that organizations rely on to manage risk in creating, preserving and realizing value. The original 2004 framework encompasses, but does not replace, the Internal Control - Integrated Framework published by COSO in 1992. The 2004 framework was also updated in 2013 to address the struggles companies were facing in implementation, mainly due to the distraction of complying with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX).
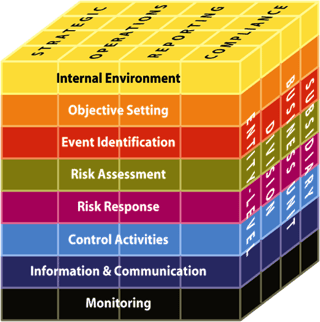
Like its internal control counterpart, the ERM framework is presented in the form of a three-dimensional matrix. The matrix includes four categories of objectives across the top—strategic, operations, reporting and compliance. There are eight components of enterprise risk management, which are further explained below.
Finally, the entity, its divisions and business units are depicted as the third dimension of the matrix for applying the framework.
Finally, the entity, its divisions and business units are depicted as the third dimension of the matrix for applying the framework.
According to COSO, the new framework:
- Provides greater insights into strategy and the role of ERM in setting and executing strategy;
- Enhances alignment between organizational performance and ERM;
- Accomodates expectations for governance and oversight;
- Recognizes the continued globalization of markets and operations and the need to apply a common, albeit tailored, approach across geographies;
- Presents fresh ways to view risk in the context of greater business complexity;
- Expands risk reporting to address expectations for greater stakeholder transparency; and
- Accommodates evolving technologies and the growth of data analytics in supporting decision-making.
See “Updated COSO ERM Framework: What's New?" for details on why the COSO ERM Framework needed to be updated and how the focus is now on what is really important in making enterprise risk management work within an organization.
As outlined by COSO, the framework provides eight components for use when evaluating ERM:
1. Internal Environment
The internal environment sets the foundation for how risk is viewed and addressed by an entity’s people, including risk philosophy and risk appetite, integrity, ethical values, and the environment in which they operate.
2. Objective-Setting
Objectives must exist before management can identify potential events affecting their achievement. ERM ensures that management has in place a process to set objectives and that the chosen objectives support and align with the entity’s mission and are consistent with its risk appetite.
3. Event Identification
Internal and external events affecting the achievement of an entity’s objectives must be identified, distinguishing between risks and opportunities.
4. Risk Assessment
Risks are analyzed, considering likelihood and impact, as a basis for determining how they should be managed. Risks are assessed on an inherent and a residual basis.
5. Risk Response
Management selects risk responses—avoiding, accepting, reducing or sharing risk—developing a set of actions to align risks with the entity’s risk tolerances and risk appetite.
6. Control Activities
Policies and procedures are established and implemented to help ensure the risk responses are effectively carried out.
7. Information and Communication
Relevant information is identified, captured and communicated in a form and timeframe that enable people to carry out their responsibilities. Effective communication also occurs in a broader sense, flowing down, across and up the entity.
8. Monitoring
The entire ERM process is monitored, and modifications made as necessary. Monitoring is accomplished through ongoing management activities, separate evaluations or both.
References :
http://info.knowledgeleader.com/bid/163293/what-is-the-coso-enterprise-risk-management-frameworkErizal Wibisono S/C1L014026
Sabtu, 04 Maret 2017
Audit : internal control
Why in audit we must understand and test internal control in a entity ?
Because, in an entity must have had SOP
(standard operasional procedures) to carry out its activities. what is the
significance of the SOP (standard operasional
procedures) ? SOP
(standard operasional procedures) is very important for an entity one of them is
to perform internal control before to do the
external audit. so, now SOP (standard operasional procedures) must also be understood by those involved in the entity to carry out the
activities therein. the conclusion is audit must understand and test the control of an
entity's internal audit in order to determine whether it is correct to
implement and adhere to the SOP
(standard operasional procedures) that
has been made by an entity.
Erizal Wibisono S (C1L014026)
Accounting International Program
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)








